What are examples of random errors?
An example of random error is putting the same weight on an electronic scales several times and obtaining readings that vary in random fashion from one reading to the next. The differences between these readings and the actual weight correspond to the random error of the scale measurements.
What is an example of a random error in chemistry?
Often random error determines the precision of the experiment or limits the precision. For example, if we were to time a revolution of a steadily rotating turnable, the random error would be the reaction time.
What are examples of random error in epidemiology?
In epidemiology, sometimes our measurements rely on a human other than the study participant measuring something on or about the participant. Examples would include measured height or weight, blood pressure, or serum cholesterol.
What are examples of random vs systematic error?
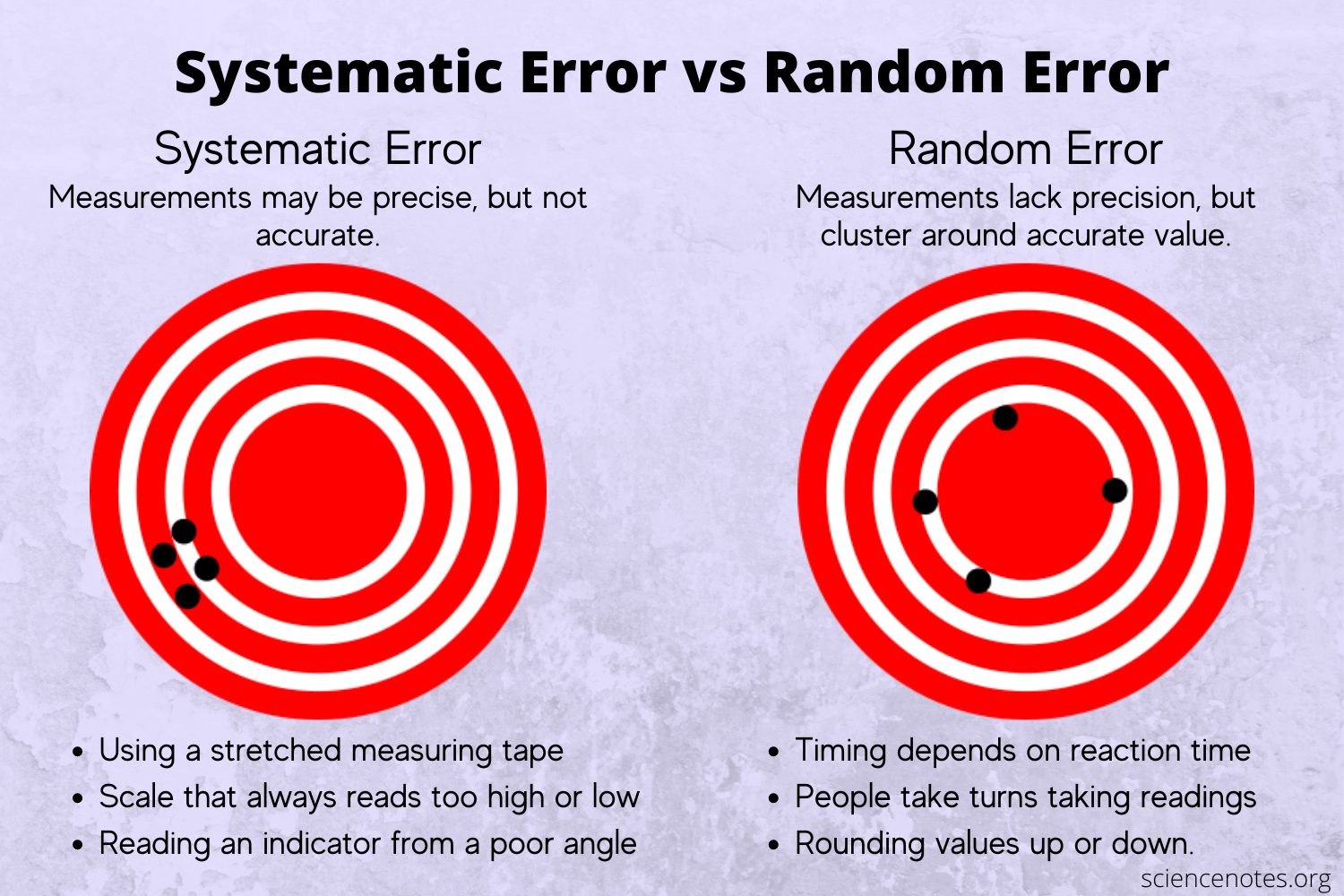
Systematic errors are consistently in the same direction (e.g. they are always 50 g, 1% or 99 mm too large or too small). In contrast, random errors produce different values in random directions. For example, you use a scale to weigh yourself and get 148 lbs, 153 lbs, and 132 lbs.
What are random errors Class 11?
Random Errors: When repeated measurements of the quantity yield different results under the same conditions, this is referred to as random error. This random error occurs for unknown reasons.
Is human error a random error?
Random errors usually result from human errors and from accidental errors. Accidental errors are brought about by changing experimental conditions that are beyond the control of the experimenter; examples are vibrations in the equipment, changes in the humidity, fluctuating temperature, etc.
What is a random error in measurement?
A random measurement error is one that stems from fluctuation in the conditions within a system being measured which has nothing to do with the true signal being measured.
What is random error in psychology?
random error error that is due to chance alone. Random errors are nonsystematic and occur arbitrarily when unknown or uncontrolled factors affect the variable being measured or the process of measurement. Such errors are generally assumed to form a normal distribution around a true score.
What are 3 examples of systematic errors?
Systematic Error Example and Causes Typical causes of systematic error include observational error, imperfect instrument calibration, and environmental interference. For example: Forgetting to tare or zero a balance produces mass measurements that are always “off” by the same amount.
What is random error also known as?
Random error is also known as variability, random variation, or ‘noise in the system'. The heterogeneity in the human population leads to relatively large random variation in clinical trials. Systematic error or bias refers to deviations that are not due to chance alone.
What are random errors in scientific method?
Random error occurs due to chance. There is always some variability when a measurement is made. Random error may be caused by slight fluctuations in an instrument, the environment, or the way a measurement is read, that do not cause the same error every time.
Is human error a random error?
Random errors usually result from human errors and from accidental errors. Accidental errors are brought about by changing experimental conditions that are beyond the control of the experimenter; examples are vibrations in the equipment, changes in the humidity, fluctuating temperature, etc.
What are examples of random vs systematic error?
Systematic errors are consistently in the same direction (e.g. they are always 50 g, 1% or 99 mm too large or too small). In contrast, random errors produce different values in random directions. For example, you use a scale to weigh yourself and get 148 lbs, 153 lbs, and 132 lbs.
What is also called random errors?
Random error is also known as variability, random variation, or ‘noise in the system'. The heterogeneity in the human population leads to relatively large random variation in clinical trials. Systematic error or bias refers to deviations that are not due to chance alone.
What is random error known as Mcq?
Random errors are also known as residual errors.
Is zero error a systematic error?
Systematic errors in experimental observations usually come from the instruments which are used in measuring. So, zero error is recognized as the systematic error.
What is the formula for random error?
It measures the random error or the statistical uncertainty of the individual measurement ti: s = Ö[SNi=1(ti – átñ)2 / (N-1) ]. About two-thirds of all the measurements have a deviation less than one s from the mean and 95% of all measurements are within two s of the mean.
Is parallax error a random error?
Reaction time errors and parallax errors are examples of random errors.
What is a zero error?
zero error Any indication that a measuring system gives a false reading when the true value of a measured quantity is zero, eg the needle on an ammeter failing to return to zero when no current flows. A zero error may result in a systematic uncertainty.
Is air bubbles a systematic error?
In determining the volume of the irregularly shaped object, any air bubbles sticking to the surface of the object when it is submerged cause systematic errors.
What is random error in pharmaceutical chemistry?
Errors fall into two basic categories:- Indeterminate (or random) errors are caused by uncontrollable or unknown fluctuations in variables that may affect experimental results. Indeterminate or accidental errors can arise from uncertainties in measurements.
Is accuracy a random error?
Accuracy measures how close measurements are to the “correct” value, and is a stronger statement than precision, as it includes both random and systematic errors. To assess accuracy the true result must already be known.
What are examples of systematic error in psychology?
error in which the data values obtained from a sample deviate by a fixed amount from the true values within the population. For example, a scale that repeatedly provides readings 0.5 g lower than the true weight would be demonstrating systematic error.
What kind of error is human error?
A human error is an action or decision which was not intended. A violation is a deliberate deviation from a rule or procedure. HSG 48 provides a fuller description of types of error, but the following may be a helpful introduction.
Is genetic error random?
While some genetic mutations can lead to genetic conditions, most mutations don't cause symptoms in humans. It's difficult to prevent mutations from happening, especially as genetic mutations can occur randomly, some without being present in your family history.
What is random error in pharmaceutical chemistry?
Errors fall into two basic categories:- Indeterminate (or random) errors are caused by uncontrollable or unknown fluctuations in variables that may affect experimental results. Indeterminate or accidental errors can arise from uncertainties in measurements.