What GPS system does the military use?
The NAVSTAR Global Positioning System (GPS) is a space-based, Joint-service program led by the Air Force that distributes Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT) data to tactical and strategic organizations.
Is military GPS the same as civilian GPS?
Is military GPS more accurate than civilian GPS? The user range error (URE) of the GPS signals in space is actually the same for the civilian and military GPS services. However, most of today's civilian devices use only one GPS frequency, while military receivers use two.
Does the US military use GPS?
GPS has two levels of service: Standard Positioning Service, available free worldwide, and Precise Positioning Service, which is restricted to U.S. armed forces and federal agencies and to selected allies.
What GPS does the Marine Corps use?
Keyed Precise Positioning System (PPS) Selective Availability Anti-Spoofing Module (SAASM) GPS User Equipment (UE) (e.g. the Defense Advanced GPS Receiver (DAGR)) and Military-Code GPS User Equipment (MGUE) that provide Precise Positioning Service deliver enhanced assurance and exclusive use of GPS for authorized …
How accurate is the US military GPS?
The first is the Coarse Acquisition signal, or C/A-code. Designed for nonmilitary users, it provides position information accurate to about 100 meters. The second signal is the encrypted Precision signal, or P-code. Intended for US military or other authorized recipients, it is accurate to within twenty meters.
Does the US military use GPS?
GPS has two levels of service: Standard Positioning Service, available free worldwide, and Precise Positioning Service, which is restricted to U.S. armed forces and federal agencies and to selected allies.
Which GPS is most accurate?
The SMAJAYU GNSS Surveying Rover System is the most accurate handheld GPS device for surveying. It features high-precision, fast-tracking RTK-GPS technology and supports survey-grade antennas for accuracy down to the centimeter range.
Why is military GPS more accurate?
Military GPS has really precise accuracy due to its use of two frequencies. The dual-frequency signal corrects for distortions from Earth's atmosphere, giving military users a more accurate location. On the other hand, civilian GPS devices only use one frequency, making the result less accurate.
Is GLONASS better than GPS?
In terms of positional accuracy GPS is slightly better than GLONASS overall, but due to the different positioning of the GLONASS satellites, GLONASS has better accuracy at high latitudes (far north or south).
Does Russia use GPS?
‘Global Navigation Satellite System') is a Russian satellite navigation system operating as part of a radionavigation-satellite service. It provides an alternative to Global Positioning System (GPS) and is the second navigational system in operation with global coverage and of comparable precision.
Who controls GPS satellites?
Currently 31 GPS satellites orbit the Earth at an altitude of approximately 11,000 miles providing users with accurate information on position, velocity, and time anywhere in the world and in all weather conditions. GPS is operated and maintained by the Department of Defense (DoD).
Do special forces use GPS?
GPS is routinely used by special operations forces (SOF) to support positioning, navigation and timing (PNT) as well as strategic satellite communications (SATCOM) providing high capacity reach back to headquarters often located hundreds if not thousands of miles away.
Can military GPS be jammed?
Military Y-Code receivers are extremely well protected from spoofing by their Selective Availability Anti-spoofing Modules (SAASMs), which leaves GPS Jamming.
What is the military GPS frequency?
GPS signals are kept in agreement with the Coordinated Universal Time scale maintained by the United States Naval Observatory, UTC(USNO). Nearly all GPSDOs use the coarse acquisition (C/A) code on the L1 carrier frequency (1575.42 MHz) as their incoming reference signal.
Is military GPS encrypted?
One of the United States Air Force's plans to modernize the Global Positioning System included introducing encrypted M-code signals that enhance anti-jamming and spoofing protection. So the M code is a powerful, highly secure military code signal that is more secure than the GPS signals used today.
How accurate is AGPS?
Very High accuracy (typically 5m-50m). Line of sight to three satellites is not required as in regular GPS technology, but two satellites must be visible for a precise AGPS fix.
Can you jam military GPS?
Military receivers use encrypted GPS signals to ensure that they are receiving an authentic signal – so these are secure in that they can't be spoofed, Fischer points out. A common misconception, however, is that a secure military GPS receiver is immune to jamming. “It's easy to jam even the encrypted signal,” he adds.
How does GPS work in the military?
Accuracy of GPS may vary from few meters to few tens of meters, which meets the military needs for navigational purposes. However, for precise location of targets for aerial bombings, missile strike etc accuracy to a level of mm is required. This can be achieved through Differential GPS (DGPS).
Are there different types of GPS?
The 3 types of GPS are: Personal GPS. Commercial GPS. Military GPS.
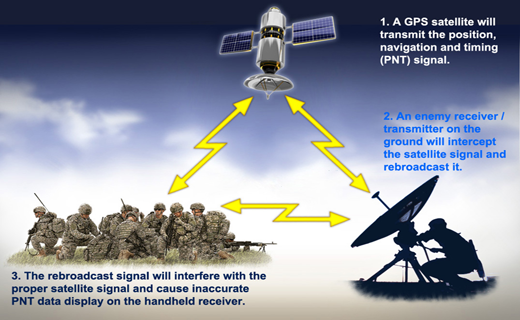
Can military GPS be spoofed?
GPS spoofing can direct aircraft, ships, or ground forces off-course and into danger. The best solution to spoofing is encryption: Current military GPS receivers use a selective availability anti-spoofing module (SAASM) to decrypt the P(Y)-code.
Does the US military use GPS?
GPS has two levels of service: Standard Positioning Service, available free worldwide, and Precise Positioning Service, which is restricted to U.S. armed forces and federal agencies and to selected allies.
How accurate is the GPS in India?
Is GPS 100% accurate?
The GPS unit is normally accurate to within two meters Circular Error Probability (CEP), and the accuracy is further increased through algorithms built into GPS Insight. Analysis of the GPS information provided by GPS Insight yields an accuracy rate of approximately 99.88%.
How does UPSC GPS work?
These satellites transmit three bits of information – the satellite's number, its position in space, and the time the information is sent. These signals are picked up by the GPS receiver, which uses this information to calculate the distance between it and the GPS satellites.
How many satellites are needed for GPS?
It takes four GPS satellites to calculate a precise location on the Earth using the Global Positioning System: three to determine a position on the Earth, and one to adjust for the error in the receiver's clock.
How many US GPS satellites are there?
Satellite Navigation is based on a global network of satellites that transmit radio signals from medium earth orbit. Users of Satellite Navigation are most familiar with the 31 Global Positioning System (GPS) satellites developed and operated by the United States.