What is a layer 3 network connection?
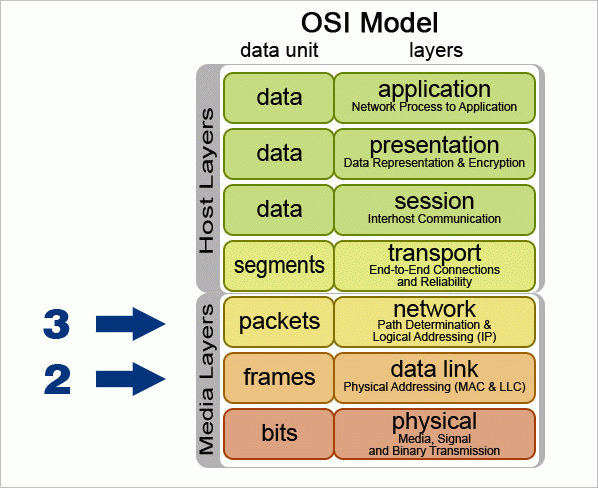
Layer 3 of the OSI Model: Network Layer provides the functional and procedural means of transferring variable length data sequences from a source host on one network to a destination host on a different network, while maintaining the quality of service requested by the transport layer (in contrast to the data link …
What is an example of network layer 3?
Network layer, layer 3. The most significant protocol at layer 3 (also called the network layer) is the Internet Protocol, or IP. IP is the standard for routing packets across interconnected networks–hence, the name internet.
What is Layer 2 vs Layer 3 networking?
Layer 2, known as the Data Link Layer, provides node-to-node data transfer with MAC address identification. All nodes on a layer 2 network are visible to one another. Ethernet switches are a common layer 2 example. Layer 3, known as the Network Layer routes data packets to specific nodes identified by IP addresses.
Is WIFI a Layer 3?
Wi-Fi operates at layer 2 and roaming is essentially a layer 2 process.
What is Layer 3 in TCP?
TCP/IP Network Layer (Layer 3) Layer 3 is the Network or Internet layer. When transmitting data, this layer adds a header containing the source and destination IP addresses to the to the data received from the Transport layer. The packet it creates will then be forwarded to the MAC or Data Link layer.
Is TCP IP a Layer 3?
TCP and UDP are both very well-known protocols, and they exist at Layer 4. TCP favors data quality over speed, whereas UDP favors speed over data quality. Layer 3 (Network) transmits data segments between networks in the form of packets.
Is Ethernet a Layer 3?
The Layer 2 protocol you're likely most familiar with is Ethernet. Devices in an Ethernet network are identified by a MAC (media access control) address, which is generally hardcoded to a particular device and doesn't normally change. Layer 3 is the network layer and its protocol is the Internet Protocol or IP.
Is VPN a Layer 2 or 3?
Layer 2 VPNs virtualize the datalink layer (Layer 2) so as to make geographically remote sites look as if they were operating in the same LAN network. Layer 3 VPNs virtualize the network layer (Layer 3) so as to route your customer networks over a public infrastructure like Internet or Service provider backbone.
Is router a Layer 2 or 3?
The most common Layer 3 device used in a network is the router. A router is able to look into the Layer 3 portion of traffic passing through it (the source and destination IP addresses) to decide how it should pass that traffic along.
Is Wan a Layer 3?
A L3 WAN means that there's routing involved in the WAN itself. This means your next-hop will be your WAN device and not the other end of the WAN. Both ends of the WAN are in different IP subnets. Examples of L3 WAN could be MPLS L3 VPN.
Are routers Layer 3 or 4?
In the OSI model, we learnt that Switches belong to Layer 2 while Routers belong to Layer 3.
Is Ethernet a layer 1 or 2?
Layer 1: Physical Layer Some protocols operate in multiple layers. Ethernet is an example. In Layer 1, it utilizes physical cabling and radio frequency standards along with the conversion of data to bits.
Is firewall a Layer 3?
A firewall generally works at layer 3 and 4 of the OSI model. Layer 3 is the Network Layer where IP works and Layer 4 is the Transport Layer, where TCP and UDP function. Many firewalls today have advanced up the OSI layers and can even understand Layer 7 – the Application Layer.
What is Layer 3 LAN port?
A Layer 3 port uses logical addresses and is used for communicating between devices on different IP networks. It is used for routing. To send data to a locally connected device (i.e. on the same IP network) the Layer 3 device encapsulates packets into Layer 2 frames.
Is VPN a layer 3?
Layer 3 VPN (L3VPN) is a type of VPN mode that is built and delivered on OSI layer 3 networking technologies. The entire communication from the core VPN infrastructure is forwarded using layer 3 virtual routing and forwarding techniques. Layer 3 VPN is also known as virtual private routed network (VPRN).
What are the three 3 types of network?
LAN (Local Area Network) MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) WAN (Wide Area Network)
Is Wan a layer 3?
A L3 WAN means that there's routing involved in the WAN itself. This means your next-hop will be your WAN device and not the other end of the WAN. Both ends of the WAN are in different IP subnets. Examples of L3 WAN could be MPLS L3 VPN.
Is IPsec a Layer 3?
What is IPsec? IPsec helps keep private data secure when it is transmitted over a public network. More specifically, IPsec is a group of protocols that are used together to set up secure connections between devices at layer 3 of the OSI model (the network layer).
Is Ping a Layer 3 protocol?
The ping command uses the services of the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), the latter being encapsulated in the IP header. Therefore, the ping utility operates basically on layer 3 (the Network layer) of the OSI model.
What is Layer 4 in networking?
Layer 4 of the OSI Model: Transport Layer provides transparent transfer of data between end users, providing reliable data transfer services to the upper layers. The transport layer controls the reliability of a given link through flow control, segmentation and desegmentation, and error control.
Is VLAN a Layer 3?
Since VLANs exist in their own layer 3 subnet, routing will need to occur for traffic to flow in between VLANs. This is where a layer 3 switch can be utilized. A Layer 3 switch is basically a switch that can perform routing functions in addition to switching.
Is WiFi a Layer 2?
As a rule of thumb, WiFi (802.11) operates at the first two layers of the OSI model, in other words, the physical layer and the data link layer.
Is OpenVPN a Layer 3?
OpenVPN by default operates in layer 3 mode (also called tun or routing mode) where it can take for example TCP and UDP packets and transfer them through the VPN tunnel to a target location.
Is VPN a layer 4?
As a rule, a traditional VPN sits on Layer 3, the network lay- er, and primarily applies the IPsec standard.
Is MPLS a Layer 2 or 3?
MPLS is considered a layer 2.5 networking protocol. Layer 2 carries IP packets over simple LANs or point-to-point WANs, while layer 3 uses internet-wide addressing and routing using IP protocols. MPLS sits in between, with additional features for data transport across the network.
Is a router layer 4?
Again, no. Routing does not involve the layer-4 header.