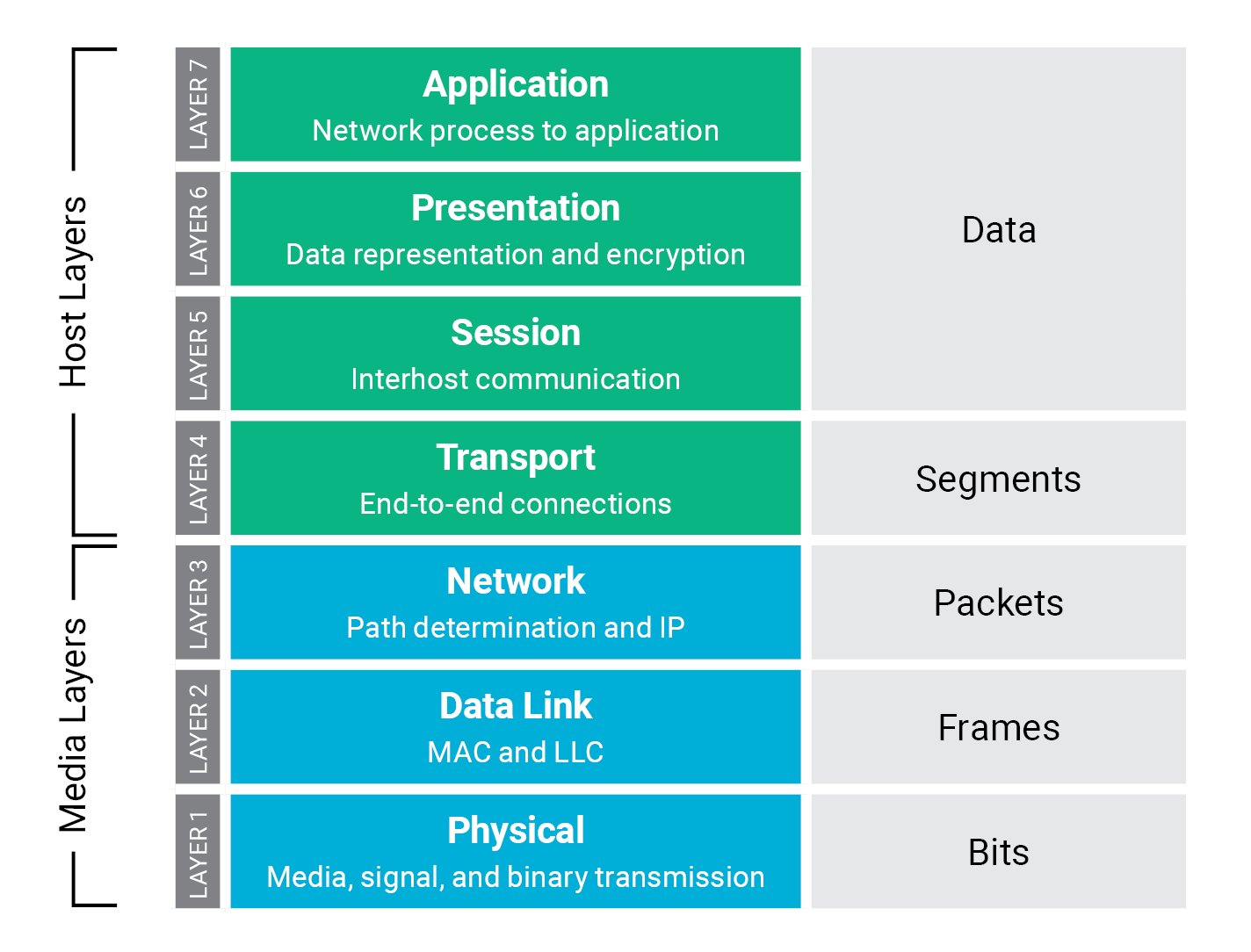
What is Layer 3 and Layer 4 network?
Layer 4 (Transport): This layer coordinates data transfer between system and hosts, including error-checking and data recovery. Layer 3 (Network): This layer determines how data is sent to the receiving device. It's responsible for packet forwarding, routing, and addressing.
What is Layer 4 networking?
Layer 4 of the OSI model, also known as the transport layer, manages network traffic between hosts and end systems to ensure complete data transfers. Transport-layer protocols such as TCP, UDP, DCCP, and SCTP are used to control the volume of data, where it is sent, and at what rate.
Is a router layer 3 or layer 4?
Network Layer of the OSI Model The network layer receives requests from the transport layer (Layer 4) and sends requests to the data link Layer (Layer 2). A router is a commonly utilised Layer 3 device. Operating at Layer 3, a router will inspect the IP and IPX addresses of incoming data packets.
What is layer 3 vs 4 vs 7?
Layer 3 deals with traffic flow, IP addresses and routing. Layer 4 covers how end-to-end communication is governed, tracks active network connections, and allows or denies traffic based on the state of the sessions. Layer 7 is the application layer, e.g. web and mail, is concerned with the content of the data packets.
What does layer 3 mean in networking?
Layer 3, the network layer, is most commonly known as the layer where routing takes place. A router's main job is to get packets from one network to another. Layer 3 protocols and technologies allow for network-to-network communications.
What is an example of layer 4?
Typical examples of layer 4 are the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
What are Layer 4 protocols?
Transport layer, layer 4. Unlike layer 3, there are really only two protocols of note found in layer 4: Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
Is firewall a layer 4?
A firewall generally works at layer 3 and 4 of the OSI model. Layer 3 is the Network Layer where IP works and Layer 4 is the Transport Layer, where TCP and UDP function. Many firewalls today have advanced up the OSI layers and can even understand Layer 7 – the Application Layer.
Is HTTP a layer 4?
HTTP is the predominant Layer 7 protocol for website traffic on the Internet. Layer 7 load balancers route network traffic in a much more sophisticated way than Layer 4 load balancers, particularly applicable to TCP‑based traffic such as HTTP.
What layer is DNS?
We know what DNS is, but what about the DNS layer? At a high level, the DNS protocol operates (using OSI model terminology) at the application level, also known as Layer 7. This layer is shared by HTTP, POP3, SMTP, and a host of other protocols used to communicate across an IP network.
Is WIFI a layer 3?
Wi-Fi operates at layer 2 and roaming is essentially a layer 2 process.
What is l3 vs l4 firewall?
Layer 3 firewalls (i.e. packet filtering firewalls) filter traffic based solely on source/destination IP, port, and protocol. Layer 4 firewalls do the above, plus add the ability to track active network connections, and allow/deny traffic based on the state of those sessions (i.e. stateful packet inspection).
What is Layer 7 in networking?
Layer 7 of The OSI Model: Application Layer is the OSI layer closest to the end user, which means that both the OSI application layer and the user interact directly with the software application. This layer interacts with software applications that implement a communicating component.
Is VPN a Layer 3?
Layer 3 VPN (L3VPN) is a type of VPN mode that is built and delivered on OSI layer 3 networking technologies. The entire communication from the core VPN infrastructure is forwarded using layer 3 virtual routing and forwarding techniques. Layer 3 VPN is also known as virtual private routed network (VPRN).
What is Layer 3 in TCP?
TCP/IP Network Layer (Layer 3) Layer 3 is the Network or Internet layer. When transmitting data, this layer adds a header containing the source and destination IP addresses to the to the data received from the Transport layer. The packet it creates will then be forwarded to the MAC or Data Link layer.
What is Layer 3 in OSI model?
Layer 3 of the OSI Model: Network Layer provides the functional and procedural means of transferring variable length data sequences from a source host on one network to a destination host on a different network, while maintaining the quality of service requested by the transport layer (in contrast to the data link …
What is Layer 4 vs Layer 7?
The differences between Layer 4 and Layer 7 Load Balancing are: Layer 4 uses only TCP connection from client to the server while layer 7 uses two TCP connections from client to the server. Layer 7 has application awareness whilst layer 4 only has on network and application ports.
What is Layer 4 TCP?
Layer 4 is the Transport layer. The transport layer creates virtual Transfer Control Protocol (TCP) or User Datagram Protocol (UDP) connections between network hosts. This layer sends and receives data to and from the applications running on its host.
What is Layer 5 in networking?
Layer 5 of the OSI Model: Session Layer is the layer of the ISO Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model that controls the dialogues (connections) between computers. It establishes, manages, and terminates the connections between the local and remote application.
Is TLS layer 4 or layer 5?
Because TLS operates at Layers 4 through 7 of the OSI model, as opposed to Layer 3, which is the case with IPsec, each application and each communication flow between client and server must establish its own TLS session to gain authentication and data encryption benefits.
What is Layer 4 of OSI model?
Layer 4 provides for the transparent transfer of data for users, systems, and applications and reliable data transfer services to the upper levels. Since the vast majority of our network traffic is IP-based nowadays, it's probably easiest to think about layer 4 as it relates to IP traffic specifically.
Why TCP IP has only 4 layers?
Additionally, the bottom two layers – Physical and Data Link – are combined into the Network Access layer for TCP/IP. Therefore, there are 4 layers in the TCP/IP Model. Specifically, they are the Network Access Layer, Internet Layer, Transport Layer, and Application Layer.
Is FTP a layer 4?
The two most common layer four protocols are the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). As with many Internet protocols, the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) uses the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) to provide guaranteed delivery on top of the Internet Protocol (IP).
Is BGP Layer 3 or 4?
Is TLS layer 4 or layer 5?
Because TLS operates at Layers 4 through 7 of the OSI model, as opposed to Layer 3, which is the case with IPsec, each application and each communication flow between client and server must establish its own TLS session to gain authentication and data encryption benefits.
Is SSL a Layer 4 protocol?
-SSL/TLS could arguably belong to Layer 4 (transport layer) because it sets up a session and sends data bidirectional by using an underlying transport protocol.