Why is military GPS more accurate?
However, most of today's civilian devices use only one GPS frequency, while military receivers use two. Using two GPS frequencies improves accuracy by correcting signal distortions caused by Earth's atmosphere.
What type of GPS does the military use?
The NAVSTAR Global Positioning System (GPS) is a space-based, Joint-service program led by the Air Force that distributes Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT) data to tactical and strategic organizations.
Which GPS is most accurate?
The SMAJAYU GNSS Surveying Rover System is the most accurate handheld GPS device for surveying. It features high-precision, fast-tracking RTK-GPS technology and supports survey-grade antennas for accuracy down to the centimeter range.
Why is GPS used in the military?
Global Positioning System (GPS) is one such technology. Military forces the world over are using GPS for diverse applications both during wartime and peacetime. These include navigation, targeting, rescue, guidance and facility management.
What is the frequency of the military GPS?
GPS signals are kept in agreement with the Coordinated Universal Time scale maintained by the United States Naval Observatory, UTC(USNO). Nearly all GPSDOs use the coarse acquisition (C/A) code on the L1 carrier frequency (1575.42 MHz) as their incoming reference signal.
Can you jam military GPS?
Military receivers use encrypted GPS signals to ensure that they are receiving an authentic signal – so these are secure in that they can't be spoofed, Fischer points out. A common misconception, however, is that a secure military GPS receiver is immune to jamming. “It's easy to jam even the encrypted signal,” he adds.
Is military GPS better than civilian GPS?
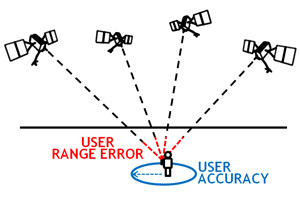
Is military GPS more accurate than civilian GPS? The user range error (URE) of the GPS signals in space is actually the same for the civilian and military GPS services. However, most of today's civilian devices use only one GPS frequency, while military receivers use two.
Can military GPS be spoofed?
GPS spoofing can direct aircraft, ships, or ground forces off-course and into danger. The best solution to spoofing is encryption: Current military GPS receivers use a selective availability anti-spoofing module (SAASM) to decrypt the P(Y)-code.
Do special forces use GPS?
GPS is routinely used by special operations forces (SOF) to support positioning, navigation and timing (PNT) as well as strategic satellite communications (SATCOM) providing high capacity reach back to headquarters often located hundreds if not thousands of miles away.
Is GPS 100% accurate?
The GPS unit is normally accurate to within two meters Circular Error Probability (CEP), and the accuracy is further increased through algorithms built into GPS Insight. Analysis of the GPS information provided by GPS Insight yields an accuracy rate of approximately 99.88%.
How accurate is the GPS in India?
How accurate is civilian GPS?
GPS is generally accurate to within 16 feet (5 meters) under open sky conditions. However, the actual accuracy can vary depending on a number of factors such as atmospheric conditions, obstructions, and the quality of the GPS receiver.
How is GPS used in war?
Signals from the twenty-four orbiting satellites that make up the GPS constellation now provide precise time and location data for all manner of US military forces–from troops creeping through unknown landscapes to precision guided munitions speeding toward their targets.
Is GLONASS better than GPS?
In terms of positional accuracy GPS is slightly better than GLONASS overall, but due to the different positioning of the GLONASS satellites, GLONASS has better accuracy at high latitudes (far north or south).
What are the advantages of GPS in marine navigation?
GPS provides the fastest and most accurate method for mariners to navigate, measure speed, and determine location.
How good is military GPS?
Military GPS has really precise accuracy due to its use of two frequencies. The dual-frequency signal corrects for distortions from Earth's atmosphere, giving military users a more accurate location.
Can military GPS be spoofed?
GPS spoofing can direct aircraft, ships, or ground forces off-course and into danger. The best solution to spoofing is encryption: Current military GPS receivers use a selective availability anti-spoofing module (SAASM) to decrypt the P(Y)-code.
How accurate is a Dagr GPS?
Single Receiver Method This would allow surveying using a single DAGR. Accuracy of 3 mils (1 mil at 1 km = 1 meter, in NATO countries it's 1/6400 of a circle). 3 MILs is about 10 arc minutes of angle.
How accurate is the GPS time reference?
Does GPS work underwater?
Nevertheless, the signals emitted by satellites cannot penetrate water. When radio waves from satellites encounter the water's surface, they merely bounce off and continue their journey through the air. Consequently, despite its widespread use as a commonplace technology, GPS does not function underwater.
What is GNSS stand for?
Global navigation satellite system (GNSS) is a general term describing any satellite constellation that provides positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) services on a global or regional basis.
Can Russia use GPS in Ukraine?
Russian forces use and need GPS. Signals from Russia's GLONASS system and terrestrial Chayka electronic navigation system are both available for use in Ukraine.
What is the alternative to GPS in the military?
NTS-3 is an experimental satellite funded by the AFRL that plans to broadcast positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) signals from geostationary Earth orbit with the goal of demonstrating next-generation PNT technologies for the U.S. military and provide an alternative to GPS.
Can China jam GPS signal?
Dana A. Goward In a conflict over Taiwan, China will almost certainly jam GPS and has the ability to damage or destroy satellites. Why It's Important: The US is far more dependent on space that China. In the region.
Which technology is better than GPS?
According to ScienceAlert, researchers have developed a new and improved technology that could eventually replace GPS in some scenarios. Called SuperGPS, it's accurate to within 10 centimetres (or 3.9 inches) and doesn't rely on navigation satellite systems.
Is A GPS more accurate than a phone?
Using the cell phone for other purposes can inadvertently cause gaps in coverage if different apps or functions create conflicts. Cell tower positioning is also less accurate than GPS satellite positioning.